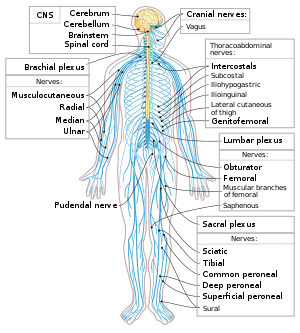
CNS disorders
| Central Nervous System Disease | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Central nervous system (yellow images of brain/spinal cord) are the affected areas | |
| Specialty |
Neurology |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|
Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS).
Every disease has different signs and symptoms. Some of them are persistent headache; pain in the face, back, arms, or legs; an inability to concentrate; loss of feeling; memory loss; loss of muscle strength; tremors; seizures; increased reflexes, spasticity, tics; paralysis; and slurred speech. One should seek medical attention if affected by these.
Any type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) or injury done to the spinal cord can result in a wide spectrum of disabilities in a person. Depending on the section of the brain or spinal cord that suffers the trauma, the outcome may be anticipated.
Infectious diseases are transmitted in several ways. Some of these infections may affect the brain or spinal cord directly. Generally, an infection is a disease that is caused by the invasion of a microorganism or virus.
Degenerative spinal disorders involve a loss of function in the spine. Pressure on the spinal cord and nerves may be associated with herniation or disc displacement. Brain degeneration also causes central nervous system diseases. Studies have shown that obese people may have severe degeneration in the brain due to loss of tissue affecting cognition.
Common structural defects include birth defects,anencephaly, hypospadias, and spina bifida. Children born with structural defects may have malformed limbs, heart problems, and facial abnormalities.
Defects in the formation of the cerebral cortex include microgyria, polymicrogyria, bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria, and pachygyria.
...
Wikipedia
