Bundesrat (Austria)
|
Federal Council Bundesrat |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type |
Upper house of the Austrian Parliament
|
| Leadership | |
|
Second President
|
|
|
Third President
|
|
| Structure | |
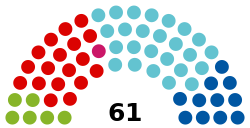
| Seats | 61 |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Government (36): Opposition (27): SPÖ (21) |
| Elections | |
| Appointment by State diets | |
|
Last election
|
No direct election |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
|
Redoute Wing (provisionally) Hofburg Imperial Palace, Vienna |
|
| Website | |
| parlament.gv.at | |
Government (36):
Opposition (27):
SPÖ (21)
The Federal Council (German: Bundesrat (pronounced [ˈbʊndəsʁaːt]) is the second chamber of the Austrian Parliament, representing the nine States of Austria (Bundesländer) on federal level. As part of a bicameral legislature alongside of the National Council (Nationalrat), it can be compared with an upper house or a senate. In fact, however, it is far less powerful than the National Council: although it has to approve every new law decided for by this "lower" chamber, the latter can—in most cases—overrule the Federal Council's refusal to approve.
The Bundesrat has its seat at the Austrian Parliament Building in Vienna, in a conclave of the former Herrenhaus chamber of the Imperial Council (Reichsrat). During a major renovation of the Parliament Building the Federal Council meets in the Hofburg.
As the Constitution of Austria (B-VG) draws a strict distinction between federal and state legislation, its Article 42 provides the Bundesrat only with the right to veto federal laws passed by the National Council. Moreover in most cases a Federal Council's veto is just suspensive, meaning the National Council can override it, passing the law again by ordinary resolution of at least half of its members. Therefore, the decisions of the Bundesrat can only delay legislation.
...
Wikipedia
