British Guiana
| British Guiana | ||||||||||||||
| Crown colony | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
Anthem God Save the Queen (1837–1901; 1952–1966) |
||||||||||||||
|
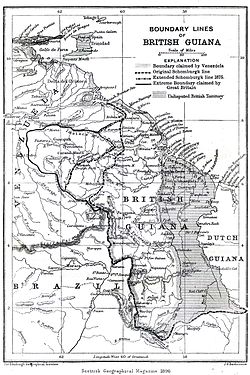
British Guiana and its boundary lines, 1896
|
||||||||||||||
| Capital | Georgetown | |||||||||||||
| Languages | English (official) Guyanese Creole |
|||||||||||||
| Government | Colony | |||||||||||||
| Historical era | New Imperialism | |||||||||||||
| • | Conquered | 1796 | ||||||||||||
| • | Anglo-Dutch Treaty | 13 August 1814 | ||||||||||||
| • | Single colony | 1831 | ||||||||||||
| • | New constitution | 1928 | ||||||||||||
| • | Independence | 26 May 1966 | ||||||||||||
| Currency |
Spanish dollar (to 1876) Guyanese dollar (to 1940s) British West Indies dollar (1935–65) East Caribbean dollar (1965–66) |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
British Guiana (also spelled Guyana) was the name of the British colony on the northern coast of South America, since 1966 known as the independent nation of Guyana. Its indigenous people are the Arawak-speaking Lucayan, part of the Taino people.
The first European to discover Guiana was Sir Walter Raleigh, an English explorer. The Dutch were the first Europeans to settle there, starting in the early 17th century, when they founded the colonies of Essequibo and Berbice, adding Demerara in the mid-18th century. In 1796, Great Britain took over these three colonies during hostilities with the French, who had occupied the Netherlands. Britain returned control to the Batavian Republic in 1802, but captured the colonies a year later during the Napoleonic Wars. The colonies were officially ceded to the United Kingdom in 1814, and consolidated into a single colony in 1831. The colony's capital was at Georgetown (known as Stabroek prior to 1812).
As the British developed the colony for sugarcane plantations, they imported many Africans as slave labour. The economy became more diversified since the late 19th century, but has relied on resource exploitation. Guyana became independent of the United Kingdom on 26 May 1966.
The English had made at least two unsuccessful attempts in the 17th century to colonise the lands that would later be known as British Guiana, at which time the Dutch had established two colonies in the area: Essequibo, administered by the Dutch West India Company, and Berbice, administered by the Berbice Association. The Dutch West India Company founded a third colony, Demerara, in the mid-18th century. During the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, when the Netherlands were occupied by the French, and Great Britain and France were at war, Britain took over the colony in 1796. A British expeditionary force was dispatched from its colony of Barbados to seize the colonies from the French-dominated Batavian Republic. The colonies surrendered without a struggle. Initially very little changed, as the British agreed to allow the long-established laws of the colonies to remain in force.
...
Wikipedia