Brachydactyly
| Brachydactyly | |
|---|---|
 |
|
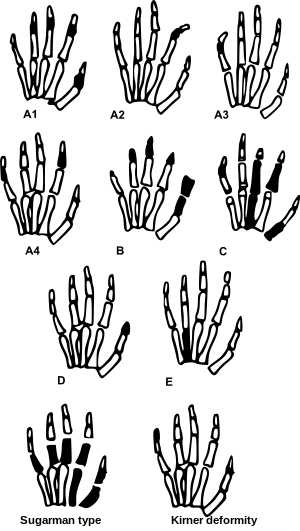
| Different forms of brachydactyly | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q68.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 755.2-755.4 |
| DiseasesDB | 29782 |
| MeSH | D059327 |
Brachydactyly (Greek βραχύς = "short" plus δάκτυλος = "finger"), is a medical term which literally means "shortness of the fingers and toes" (digits). The shortness is relative to the length of other long bones and other parts of the body. Brachydactyly is an inherited, usually dominant trait. It most often occurs as an isolated dysmelia, but can also occur with other anomalies as part of many congenital syndromes.
Nomograms for normal values of finger length as a ratio to other body measurements have been published. In clinical genetics the most commonly used index of digit length is the dimensionless ratio of the length of the 3rd (middle) finger to the hand length. Both are expressed in the same units (centimeters, for example) and are measured in an open hand from the fingertip to the principal creases where the finger joins the palm and where the palm joins the wrist. A nomogram can be found in the Appendix of Jones, ed. Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation, 5th edition, Philadelphia: Saunders (1997).
There are several types of Brachydactyly:
uniform swelling of the soft tissue of the terminal phalanx of a digit") as "clubbed thumbs".
In the above brachydactyly syndromes, short digits are the most prominent of the anomalies, but in many other syndromes (Down syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, etc.), brachydactyly is a minor feature compared to the other anomalies or problems comprising the syndrome.
...
Wikipedia
