Botolan language
| Botolan | |
|---|---|
| Botolan Sambal | |
| Native to | Philippines |
| Region | some parts of Zambales province, Luzon |
|
Native speakers
|
33,000 (2000) |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog | boto1242 |
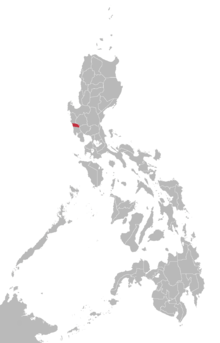
Area where Botolan Sambal is spoken according to Ethnologue
|
|
Botolan is a Sambalic language spoken by 32,867 (SIL 2000) Sambal, primarily in the Zambal municipalities of Botolan and Cabangan in the Philippines.
The Ayta people of sitio Villar, Botolan, and sitio Kakilingan, Santa Fe, Cabangan also speak a Botolan dialect with some unique lexical items.
Botolan has 20 phonemes: 16 consonants and four vowels. Syllable structure is relatively simple. Each syllable contains at least a consonant and a vowel.
Botolan has four vowels. They are:
There are five main diphthongs: /aɪ/, /uɪ/, /aʊ/, /ij/, and /iʊ/.
Below is a chart of Botolan consonants. All the stops are unaspirated. The velar nasal occurs in all positions including at the beginning of a word.
Note: Consonants /d/ and /ɾ/ can sometimes interchange as they were once allophones.
Stress is phonemic in Botolan. Stress on words is very important, they differentiate words with the same spellings, but with different meanings, e.g. hikó (I) and híko (elbow).
Many words pronounced with /s/ and /ɡ/ in Filipino have /h/ and /j/, respectively, in their cognates in Botolan. Compare hiko and bayo with the Filipino siko and bago.
...
Wikipedia
