Bortezomib
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Velcade |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607007 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Subcutaneous, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 83% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, extensively involved |
| Biological half-life | 9 to 15 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | PS-341 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.601 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
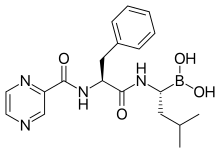
| Formula | C19H25BN4O4 |
| Molar mass | 384.237 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Bortezomib (BAN, INN and USAN; marketed as Velcade by Millennium Pharmaceuticals; Neomib by Getwell and Bortecad by Cadila Healthcare) is an anti-cancer drug and the first therapeutic proteasome inhibitor to be used in humans. Proteasomes are cellular complexes that break down proteins. In some cancers, the proteins that normally kill cancer cells are broken down too quickly. Bortezomib interrupts this process and lets those proteins kill the cancer cells. It is approved in the U.S. and Europe for treating relapsed multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. In multiple myeloma, complete clinical responses have been obtained in patients with otherwise refractory or rapidly advancing disease.
Bortezomib was originally synthesized in 1995 at Myogenics. The drug (PS-341) was tested in a small Phase I clinical trial on patients with multiple myeloma. It was brought to further clinical trials by Millennium Pharmaceuticals in October 1999.
In May 2003, seven years after the initial synthesis, bortezomib (marketed as Velcade by Millennium Pharmaceuticals Inc.) was approved in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in multiple myeloma, based on the results from the SUMMIT Phase II trial. Bortezomib is approved for initial treatment of patients with multiple myeloma by the U.S. FDA in 2008.
Later in August 2014, this Administration approved Velcade for the retreatment of adult patients with multiple myeloma who had previously responded to Velcade therapy and relapsed at least six months following completion of prior treatment.
The drug is an N-protected dipeptide and can be written as Pyz-Phe-boroLeu, which stands for pyrazinoic acid, phenylalanine and Leucine with a boronic acid instead of a carboxylic acid. Peptides are written N-terminus to C-terminus, and this convention is used here even though the "C-terminus" is a boronic acid instead of a carboxylic acid.
...
Wikipedia
