Borean languages
| Borean | |
|---|---|
| (hypothetical) | |
| Geographic distribution |
Eurasia, sometimes the Americas |
| Linguistic classification | Proposed language family |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | None |
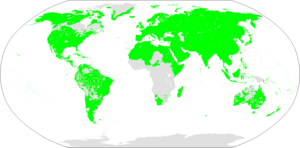
Borean macro-family according to Sergei Starostin.
|
|
Borean (also Boreal or Boralean) is a hypothetical linguistic macrofamily that encompasses almost all language families worldwide except those native to sub-Saharan Africa, New Guinea, Australia, and the Andaman Islands. Its supporters propose that the various languages spoken in Eurasia and adjacent regions have a genealogical relationship, and ultimately descend from languages spoken during the Upper Paleolithic in the millennia following the Last Glacial Maximum. The name Borean is based on the Greek , and means "northern". This reflects the fact that the group is held to include most language families native to the northern hemisphere. Two distinct models of Borean exist: that of Harold C. Fleming and that of Sergei Starostin.
The concept is due to Harold C. Fleming (1987), who proposed such a "mega-super-phylum" for the languages of Eurasia, termed Borean or Boreal in Fleming (1991) and later publications. In Fleming's model, Borean includes ten different groups: Afrasian (his term for Afroasiatic), Kartvelian, Dravidian, a group comprising Sumerian, Elamitic, and some other extinct languages of the ancient Near East, Eurasiatic (a proposal of Joseph Greenberg that includes Indo-European, Uralic, Altaic, and several other language families), Macro-Caucasian (a proposal of John Bengtson that includes Basque and Burushaski), Yeniseian, Sino-Tibetan, Na-Dene, and Amerind.
...
Wikipedia
