Body of the maxilla
| Body of maxilla | |
|---|---|
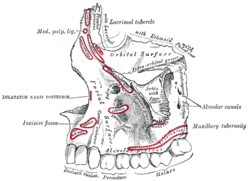
Left maxilla. Outer surface.
|
|
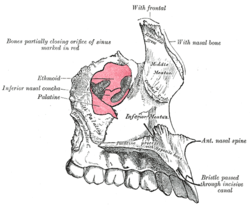
Left maxilla. Nasal surface.
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | corpus maxillae |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
c_56/12260607 |
| TA | A02.1.12.002 |
| FMA | 52846 |
|
Anatomical terms of bone
[]
|
|
The body of the maxilla is somewhat pyramidal in shape, and contains a large cavity, the maxillary sinus (antrum of Highmore). It has four surfaces; the anterior surface, the orbital or superior surface, the nasal or medial surface and the infratemporal or posterior surface.
The orbital surface of the maxilla is smooth and triangular. It forms most of the floor of the orbit, the cavity that contains the eyeball and its vessels. At its middle border is an irregular margin at the front of which is the lacrimal groove or notch, and behind this groove, the margin articulates with the thin plate of ethmoid bone (lamina papyracea) and the orbital process of the hard palate (palatine). To the side of the lacrimal notch is a depression which gives rise to the oblique inferior oculi. (obliquus oculi inferior). Its back border is a smooth rounded edge and this forms the front margin of the inferior orbital (infraorbital) fissure. This groove or fissure, carries the infraorbital vessels and nerve. Sometimes it joins at the side with part of the sphenoid bone.
The orbital surface is limited at the front by part of the orbit’s circumference. The infraorbital groove passes forward and ends in the infraorbital canal; this branches to give a second small canal that runs off from this, downwards into the front wall of the sinus where it carries the anterior superior alveolar vessels and nerve to the front teeth of the maxilla. Sometimes a second canal is given off that travels down in the lateral wall of the sinus and carries the middle alveolar nerve to the premolar teeth.
The front, or anterior surface of the maxilla is directed forwards and to the side. At its lower part are a series of small raised parts which correspond to the positions of the roots of the teeth. Above the incisor teeth locations there is a shallow depression, the incisive fossa, and this gives rise to the depressor alae nasi. Below the incisive fossa, the alveolar (tooth cavity) is attached to a segment of the orbicular oris and a little above and to the side, the nasalis muscle arises. To the side of the incisor fossa is the larger and deeper canine fossa and these are separated by a vertical ridge, the canine eminence. The canine fossa gives origin to the levator anguli oris.
...
Wikipedia
