Bluetongue virus
| Bluetongue virus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
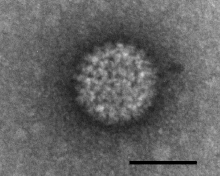
| Electron micrograph of Bluetongue virus. Scale bar = 50 nm. | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group III (dsRNA) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | Reoviridae |
| Genus: | Orbivirus |
| Species: | Bluetongue virus |
Bluetongue disease is a non-contagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle,goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by the Bluetongue virus (BTV). The virus is transmitted by the midge Culicoides imicola, Culicoides variipennis, and other culicoids.
In sheep, BTV causes an acute disease with high morbidity and mortality. BTV also infects goats, cattle and other domestic animals as well as wild ruminants (for example, blesbuck, white-tailed deer, elk, and pronghorn antelope).
Major signs are high fever, excessive salivation, swelling of the face and tongue and cyanosis of the tongue. Swelling of the lips and tongue gives the tongue its typical blue appearance, though this sign is confined to a minority of the animals. Nasal signs may be prominent, with nasal discharge and stertorous respiration.
Some animals also develop foot lesions, beginning with coronitis, with consequent lameness. In sheep, this can lead to knee-walking. In cattle, constant changing of position of the feet gives bluetongue the nickname The Dancing Disease. Torsion of the neck (opisthotonos or torticollis) is observed in severely affected animals.
Not all animals develop signs, but all those that do lose condition rapidly, and the sickest die within a week. For affected animals which do not die, recovery is very slow, lasting several months.
...
Wikipedia
