Blood typing
| Cross-matching | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
Compatibility testing concerning RBCs
|
|
| MeSH | D001788 |
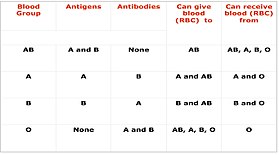
Cross-matching (or crossmatching) blood, in transfusion medicine, refers to the test that is performed prior to a blood transfusion in order to determine if the donor's blood is compatible with the blood of an intended recipient. Cross-matching is also used to determine compatibility between a donor and recipient in organ transplantation. Compatibility is determined through matching of different blood group systems, the most important of which are the ABO and Rh system, and/or by directly testing for the presence of antibodies against a sample of donor tissues or blood.
Cross-matching is done by a certified laboratory technologist, in a laboratory. It can be done electronically, with a computer database if a patient has previously been tested, or serologically by way of testing. Simpler tests may be used to determine blood type (only), or to screen for antibodies (only). (indirect Coombs test).
Immediate-spin cross-matching is an abbreviated form of cross-matching that is faster, less expensive but also less sensitive. It is an immediate test that combines the patient's serum and donor's red blood cells at room temperature. No agglutination indicates a negative test reaction, or compatible match. Indications for ISCM are dependent on the circumstances of the patient and it can be used in place of a full cross-match or performed as a preliminary test.
Electronic cross-matching is a computer-assisted analysis using data, from the donor unit (where a donor's blood is tested prior to donation) and testing done on blood samples from the intended recipient. This includes ABO/Rh typing of the unit and of the recipient, and an antibody screen of the recipient. Electronic cross-matching can only be used if a patient has a negative antibody screen, which means that they do not have any active red blood cell atypical antibodies, or they are below the detectable level of current testing methods. If all of the data entered is compatible, the computer will print a compatibility label stating that the unit is safe to transfuse.
...
Wikipedia
