Bishopric of Ermland
| Prince-Bishopric of Warmia | ||||||||||
|
Fürstbistum Ermland (de) Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie (pl) Dioecesis Varmiensis (la) |
||||||||||
| Part of the State of the Teutonic Order | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
State of the Teutonic Order, ca 1410
|
||||||||||
| Capital | Lidzbark Warmiński Heilsberg | |||||||||
| Languages | Polish, German | |||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic | |||||||||
| Government | Theocracy | |||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | |||||||||
| • |
Prussian bishoprics founded by Teutonic Knights |
1243 | ||||||||
| • | Gained Reichsfreiheit | 1356 | ||||||||
| • |
Independence from the Teutonic Order |
1466 | ||||||||
| • |
Subjugated to the Polish Crown |
1479 | ||||||||
| • | Two-thirds annexed by Prussia |
1512 | ||||||||
| • | Annexed by Prussia | August 5, 1466 | ||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Prince-Bishopric of Warmia | ||||||||||
|
Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie (pl) Fürstbistum Ermland (de) Dioecesis Varmiensis (la) |
||||||||||
| Part of Kingdom of Poland and Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Exempt Prince-Bishopric of Warmia in 1635. (In red on a map of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth)
|
||||||||||
| Capital | 1243-1945 Frauenburg, since 1972 Olsztyn (Allenstein) | |||||||||
| Languages | Latin Language, German and Polish | |||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic | |||||||||
| Government | Theocracy | |||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | |||||||||
| • | Prussian bishopric founded as protectorate of Teutonic Knights |
|||||||||
| • |
Subjugated to Polish Crown |
1479 |
||||||||
| • | Annexed by Prussia | August 5, 1772 | ||||||||
|
||||||||||
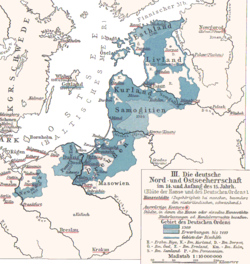
The Prince-Bishopric of Warmia (Polish: Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie,German: Fürstbistum Ermland) was a semi-independent ecclesiastical state, ruled by the incumbent ordinary of the Ermland/Warmia see and comprising one third of the then diocesan area. The other two thirds of the diocese were under the secular rule of Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights (Teutonic Prussia) (till 1525, and Ducal Prussia thereafter). The Ermland/Warmia see was a Prussian diocese under the jurisdiction of the Archbishopric of Riga that was a protectorate of Teutonic Prussia (1243–1466) and a protectorate by treaty of Poland - later part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Peace of Thorn (1466–1772)
It was founded as the Bishopric of Ermland by William of Modena in 1243 in the territory of Prussia after it was conquered by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. The diocesan cathedral chapter constituted in 1260. While in the 1280s the Teutonic Order succeeded to impose the simultaneous membership of all capitular canons in the Order in the other three Prussian bishoprics, Ermland's chapter maintained its independence. So Ermland's chapter was not subject to outside influence when electing its bishops. Thus the Golden Bull of Emperor Charles IV names the bishops as prince-bishops, a rank not awarded to the other three Prussian bishops (Culm, Pomesania, and Samland).
...
Wikipedia