Bisabolene
 α-Bisabolene
|
|
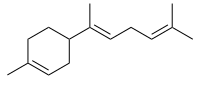
 β-Bisabolene
|
|
 β-Bisabolene
|
|
 γ-Bisabolene
|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
(α): (E)-1-Methyl-4-(6-methylhepta-2,5-dien-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene
(β): (S)-1-Methyl-4-(6-methylhepta-1,5-dien-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene (γ): (Z)-1-Methyl-4-(6-methylhept-5-en-2-ylidene)cyclohex-1-ene |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
17627-44-0 (α) 495-61-4 (β) 495-62-5 (γ) |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | (α): Interactive image (β): Interactive image (γ): Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
4509521 (α) 8279897 (β) 2298446 (γ) |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.36 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Bisabolenes are a group of closely related natural chemical compounds which are classified as sesquiterpenes. Bisabolenes are present in the essential oils of a wide variety of plants including cubeb, lemon and oregano. Various derivates also function as pheromones in different insects, such as stink bugs and fruit flies. It has also been observed to be produced by several fungi, though it's biological role in that group of organisms remains unclear.
Bisabolenes are intermediates in the biosynthesis of many other natural chemical compounds, including hernandulcin, a natural sweetener. β-Bisabolene has a balsamic odor and is approved in Europe as a food additive.
...
Wikipedia
