Bartholinitis
| Bartholin's cyst | |
|---|---|
 |
|
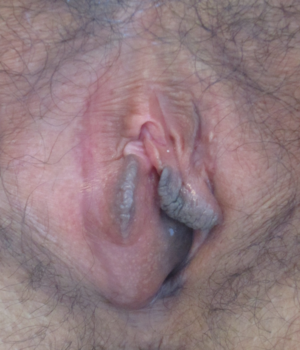
| Bartholin's cyst of the right side | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | urology |
| ICD-10 | N75.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 616.2 |
| MedlinePlus | 001489 |
A Bartholin's cyst, also known as Bartholinitis occurs when a Bartholin's gland is blocked and the gland becomes inflamed. Sizes range from that of a pea to that of an egg and form just within each side of the lower part of the opening of the vagina. An abscess may form if the cyst becomes infected. In this case it often becomes red and painful when touched.
A Bartholin's cyst is not an infection, although it can be caused by an infection, inflammation, or physical blockage (mucus or other impediment) to the Bartholin's ducts (tubes which lead from the glands to the vulva). If infection sets in, the result is a Bartholin's abscess. Cysts are not sexually transmitted. There is no known reason for their development and infection is rare. With an abscess, a bacterial infection is the cause, but it is usually not an STD.
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms. If there are no symptoms, no treatment may be needed. If a cyst is causing problems, drainage is recommended. The preferred method of drainage is the insertion of a Word catheter for four weeks. Simple incision and drainage may allow the cyst to reform. A surgical procedure known as marsupialization may be used for cysts, but should not be used if they are infected. If the problems persist, the entire gland may be removed. Removal is sometimes recommended in those older than 40 to ensure cancer is not present. Antibiotics are not generally needed.
Bartholin's cysts are most likely in women of childbearing age. About two percent of women have the problem at some point in their life.
Most Bartholin's cysts do not cause any symptoms, although some may cause pain during walking, sitting, or sexual intercourse (dyspareunia). They are usually between 1 and 4 cm, and are located just medial to the labia minora. Most Bartholin's cysts only affect the left or the right side (unilateral). Small cysts are usually not painful, but very large cysts can cause significant pain.
A Bartholin's gland cyst develops when the duct that drains the gland becomes blocked. Blockage may be caused by an infection or a mucus plug. The secretions from the Bartholin's gland are retained, forming a cyst.
...
Wikipedia
