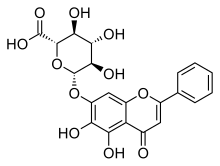
Baicalin
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-(5,6-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-chromen-7-yl)oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxy-tetrahydropyran-2-carboxylic acid
|
|
| Other names
Baicalein 7-O-glucuronide; 5,6-Dihydroxy-4-oxygen-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-7-beta-D-glucopyranose acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.133.557 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C21H18O11 | |
| Molar mass | 446.36 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 202 to 205 °C (396 to 401 °F; 475 to 478 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Baicalin is a flavone glycoside. It is the glucuronide of baicalein.
Baicalin is found in several species in the genus Scutellaria, including Scutellaria baicalensis and Scutellaria lateriflora. There are 10 mg/g baicalin in Scutellaria galericulata leaves. It is one of the chemical ingredients of Sho-Saiko-To, an herbal supplement. It is also present in the bark isolate of the Oroxylum indicum tree.
Baicalin, along with its aglycone baicalein, is a positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site and/or a non-benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. In mice, baicalin produces anxiolytic effects without sedative or myorelaxant effects. It is thought that baicalin, along with other flavonoids, may underlie the anxiolytic effects of S. baicalensis and S. lateriflora.
Baicalin is a known prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor. It induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.
...
Wikipedia
