Auditory tubes
| Eustachian Tube | |
|---|---|
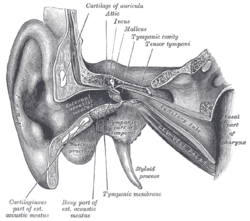
External and middle ear. Eustachian tube labelled as auditory tube
|
|
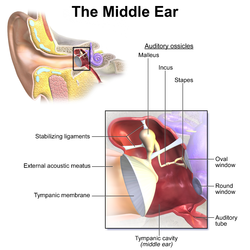
Middle ear, with auditory tube at bottom right
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | first pharyngeal pouch |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Tuba auditiva, tuba auditivea, tuba auditoria |
| MeSH | A09.246.397.369 |
| Code | 381.81 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
t_21/12826987 |
| TA | A15.3.02.073 |
| FMA | 9705 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The Eustachian tube /juːˌsteɪ.ʃən/, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear. It is a part of the middle ear. In adult humans the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi.
In humans and other land animals the middle ear (like the ear canal) is normally filled with air. Unlike the open ear canal, however, the air of the middle ear is not in direct contact with the atmosphere outside the body. The Eustachian tube connects from the chamber of the middle ear to the back of the nasopharynx.
Normally, the Eustachian tube is collapsed, but it gapes open both with swallowing and with positive pressure. When taking off in an airplane, the surrounding air pressure goes from higher (on the ground) to lower (in the sky). The air in the middle ear expands as the plane gains altitude, and pushes its way into the back of the nose and mouth. On the way down, the volume of air in the middle ear shrinks, and a slight vacuum is produced. Active opening of the Eustachian tube is required to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the surrounding atmosphere as the plane descends. A diver also experiences this change in pressure, but with greater rates of pressure change; active opening of the Eustachian tube is required more frequently as the diver goes deeper into higher pressure.
The Eustachian tube extends from the anterior wall of the middle ear to the lateral wall of the nasopharynx, approximately at the level of the inferior nasal concha. It consists of a bony part and a cartilaginous part.
The bony part (1/3) nearest to the middle ear is made of bone and is about 12 mm in length. It begins in the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity, below the septum canalis musculotubarii, and, gradually narrowing, ends at the angle of junction of the squamous and the petrous parts of the temporal bone, its extremity presenting a jagged margin which serves for the attachment of the cartilaginous part.
...
Wikipedia
