Aspergillus niger
| Aspergillus niger | |
|---|---|
 |
|
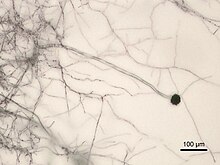
| Micrograph of A. niger grown on Sabouraud agar. | |
 |
|
| Details of the head | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. niger |
| Binomial name | |
|
Aspergillus niger van Tieghem 1867 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Aspergillus niger var. niger |
|
| NCBI genome ID | 429 |
|---|---|
| Ploidy | haploid |
| Genome size | 34 Mb |
| Number of chromosomes | 8 |
Aspergillus niger var. niger
Aspergillopsis nigra (Tiegh.) Speg.
Rhopalocystis nigra (Tiegh.) Grove
Sterigmatocystis nigra (Tiegh.) Sacc., (1877)
Aspergillus niger is a fungus and one of the most common species of the genus Aspergillus.
It causes a disease called black mould on certain fruits and vegetables such as grapes, apricots, onions, and peanuts, and is a common contaminant of food. It is ubiquitous in soil and is commonly reported from indoor environments, where its black colonies can be confused with those of Stachybotrys (species of which have also been called "black mould").
Some strains of A. niger have been reported to produce potent mycotoxins called ochratoxins; other sources disagree, claiming this report is based upon misidentification of the fungal species. Recent evidence suggests some true A. niger strains do produce ochratoxin A. It also produces the isoflavone orobol.
A. niger is included in Aspergillus subgenus Circumdati, section Nigri. The section Nigri includes 15 related black-spored species that may be confused with A. niger, including A. tubingensis, A. foetidus, A. carbonarius, and A. awamori. A number of morphologically similar species were recently described by Samson et al.
Recently the strain of ATCC 16404 Aspergillus niger has been reclassified at Aspergillus brasiliensis (refer to publication by Varga et al.). This has required an update to the U.S. Pharmacopoeia and the European Pharmacopoeia which commonly use this strain throughout the pharmaceutical industry.
A. niger causes black mold of onions and ornamental plants. Infection of onion seedlings by A. niger can become systemic, manifesting only when conditions are conducive. A. niger causes a common postharvest disease of onions, in which the black conidia can be observed between the scales of the bulb. The fungus also causes disease in peanuts and in grapes.
A. niger is less likely to cause human disease than some other Aspergillus species. In extremely rare instances, humans may become ill, but this is due to a serious lung disease, aspergillosis, that can occur. Aspergillosis is, in particular, frequent among horticultural workers who inhale peat dust, which can be rich in Aspergillus spores. It has been found in the mummies of ancient Egyptian tombs and can be inhaled when they are disturbed.
...
Wikipedia
