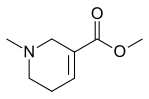
Arecoline
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
63-75-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2230 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 296 |
| DrugBank |
DB04365 |
| ChemSpider |
13872064 |
| UNII |
4ALN5933BH |
| KEGG |
C10129 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:2814 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL7303 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.514 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 155.194 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Density | 1.0495 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 209 °C (408 °F) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arecoline (/əˈrɛkəliːn/) is a nicotinic acid-based alkaloid found in the areca nut, the fruit of the areca palm (Areca catechu). It is an odourless oily liquid.
Arecoline is a base, and its conjugate acid has a pKa ~ 6.8. Arecoline is volatile in steam, miscible with most organic solvents and water, but extractable from water by ether in presence of dissolved salts. Being basic, arecoline forms salts with acids. The salts are crystalline, but usually deliquescent: the hydrochloride, arecoline•HCl, forms needles, m.p. 158 °C; the hydrobromide, arecoline•HBr, forms slender prisms, mp. 177-179 °C from hot alcohol; the aurichloride, arecoline•HAuCl4, is an oil, but the platinichloride, arecoline2•H2PtCl6, mp. 176 °C, crystallizes from water in orange-red rhombohedrons. The methiodide forms glancing prisms, mp. 173-174 °C.
In many Asian cultures, the areca nut is chewed along with betel leaf to obtain a stimulating effect. Arecoline is the primary active ingredient responsible for the central nervous system effects of the areca nut. Arecoline has been compared to nicotine; however, nicotine acts primarily on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Arecoline is known to be a partial agonist of muscarinic acetylcholine M1, M2, M3 receptors and M4, which is believed to be the primary cause of its parasympathetic effects (such as pupillary constriction, bronchial constriction, etc.).
...
Wikipedia
