Archaeal
| Archaea (Archaebacteria) Temporal range: Paleoarchean or perhaps Eoarchean – recent |
|
|---|---|
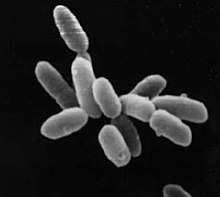 |
|
|
Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1, each cell about 5 μm long |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: |
Archaea Woese, Kandler & Wheelis, 1990 |
| Kingdoms and phyla | |
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The Archaea (/ɑːrˈkiːə/ or /ɑːrˈkeɪə/ ar-KEE-ə or ar-KAY-ə) constitute a domain and kingdom of single-celled microorganisms. These microbes (archaea; singular archaeon) are prokaryotes, meaning that they have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles in their cells.
Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this classification is outdated. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains of life, Bacteria and Eukaryota. The Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because the majority have not been isolated in the laboratory and have only been detected by analysis of their nucleic acids in samples from their environment.
...
Wikipedia
