Antinociceptic
| Nociceptor | |
|---|---|
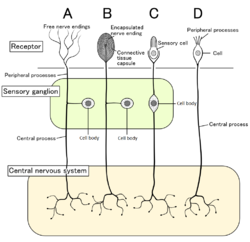
Four types of sensory neurons and their receptor cells. Nociceptors shown as free nerve endings type A
|
|
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
A nociceptor is a type of receptor at the end of a sensory neuron's axon that responds to damaging or potentially damaging stimuli by sending possible threat signals to the spinal cord and the brain. If the brain thinks the threat is credible, it creates the sensation of pain to direct attention to the body part, so the threat can hopefully be mediated. This process is called nociception.
Nociceptors were discovered by Charles Scott Sherrington in 1906. In earlier centuries, scientists believed that animals were like mechanical devices that transformed the energy of sensory stimuli into motor responses. Sherrington used many different experiments to demonstrate that different types of stimulation to an afferent nerve fiber's receptive field led to different responses. Some intense stimuli trigger reflex withdrawal, certain autonomic responses, and pain. The specific receptors for these intense stimuli were called nociceptors.
In mammals, nociceptors are found in any area of the body that can sense noxious stimuli. External nociceptors are found in tissue such as the skin (cutaneous nociceptors), the corneas, and the mucosa. Internal nociceptors are found in a variety of organs, such as the muscles, the joints, the bladder, the gut, and the digestive tract. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in either the dorsal root ganglia or the trigeminal ganglia. The trigeminal ganglia are specialized nerves for the face, whereas the dorsal root ganglia are associated with the rest of the body. The axons extend into the peripheral nervous system and terminate in branches to form receptive fields.
...
Wikipedia
