Antimycin A
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
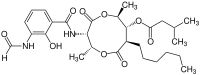
(2R,3S,6S,7R,8R)-3-[(3-Formamido-2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]-8-hexyl-2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1,5-dioxonan-7-yl 3-methylbutanoate
|
|
| Other names
Fintrol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
642-15-9 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:22584 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL211501 |
| ChemSpider |
14246 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.279 |
| MeSH | Antimycin+A |
| PubChem | 14957 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C28H40N2O9 | |
| Molar mass | 548.63 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Antimycins are a group of secondary metabolites produced by Streptomyces bacteria. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
Antimycin A is the active ingredient in Fintrol, a chemical piscicide (fish poison) used in fisheries management.
Antimycin A binds to the Qi site of , thereby inhibiting the oxidation of ubiquinone in the Qi site thereby disrupting the Q-cycle of enzyme turn over. is a central enzyme in the electron transport chain of oxidative phosphorylation. The inhibition of this reaction disrupts the formation of the proton gradient across the . The production of ATP is subsequently inhibited, as protons are unable to flow through the ATP synthase complex in the absence of a proton gradient. This inhibition also results in the formation of quantities of the toxic free radical superoxide.
It has also been found to inhibit the cyclic electron flow within photosynthetic systems along the proposed ferredoxin quinone reductase pathway.
Fungus-growing attine ants have been shown to use antimycins - produced by symbiotic Streptomyces bacteria - in their fungiculture, to inhibit non-cultivar (i.e. pathogenic) fungi. One research group studying these symbiotic Streptomyces bacteria recently identified the biosynthetic gene cluster for antimycins, which was unknown despite the compounds themselves being identified 60 years ago. Antimycins are synthesised by a hybrid polyketide synthase (PKS)/non-ribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS).
...
Wikipedia
