Anterior spinal artery syndrome
| Anterior spinal artery syndrome. | |
|---|---|
 |
|
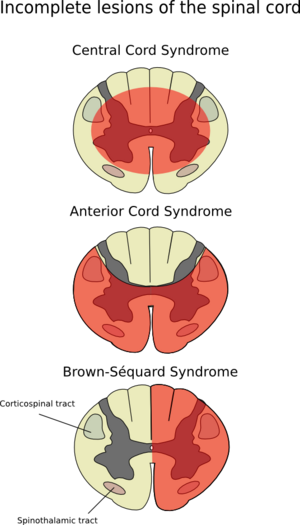
| Anterior cord syndrome is central diagram | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | cardiology |
| ICD-10 | I65.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 433.8 806.02, 806.07, 806.12, 806.17, 806.22, 806.27, 806.32, 806.37 |
| DiseasesDB | 33437 |
| eMedicine | neuro/348 |
| MeSH | D020759 |
Anterior spinal artery syndrome (also known as "anterior spinal cord syndrome") is a medical condition where the anterior spinal artery, the primary blood supply to the anterior portion of the spinal cord, is interrupted, causing ischemia or infarction of the spinal cord in the anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord and medulla oblongata. It is characterized by loss of motor function below the level of injury, loss of sensations carried by the anterior columns of the spinal cord (pain and temperature), and preservation of sensations carried by the posterior columns (fine touch, vibration and proprioception). Anterior spinal artery syndrome is the most common form of spinal cord infarction.
The anterior portion of the spinal cord is supplied by the anterior spinal artery. It begins at the foramen magnum where branches of the two vertebral arteries exit, merge, and descend along the anterior spinal cord. As the anterior spinal artery proceeds inferiorly, it receives branches originating mostly from the aorta. The largest aortic branch is the artery of Adamkiewicz.
Symptoms usually occur very quickly and are often experienced within one hour of the initial damage. MRI can detect the magnitude and location of the damage 10–15 hours after the initiation of symptoms. Diffusion-weighted imaging may be used as it is able to identify the damage within a few minutes of symptomatic onset.
Clinical features include paraparesis or quadriparesis (depending on the level of the injury) and impaired pain and temperature sensation. Complete motor paralysis below the level of the lesion due to interruption of the corticospinal tract, and loss of pain and temperature sensation at and below the level of the lesion. Proprioception and vibratory sensation is preserved, as it is in the dorsal side of the spinal cord.
...
Wikipedia
