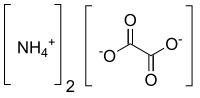
Ammonium oxalate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Diammonium ethanedioate
|
|
| Other names
Diammonium oxalate
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
1113-38-8 6009-70-7 (monohydrate) |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:91241 |
| ChemSpider |
13577 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.912 |
| PubChem | 14213 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C2H8N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 124.10 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 70 C (158 F, 343.15 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium oxalate, C2H8N2O4 – more commonly written as (NH4)2C2O4 – is an oxalate salt with ammonium (sometimes as a monohydrate). It is a colorless (white) salt under standard conditions and is odorless and non-volatile. It is the ammonium salt of oxalic acid, and occurs in many plants and vegetables. It is produced in the body by metabolism of glyoxylic acid or ascorbic acid. It is not metabolized but excreted in the urine. It is a constituent of some types of kidney stone. It is also found in guano.
Ammonium oxalate is used as an analytical reagent and general reducing agent. It and other oxalates are used as anticoagulants, to preserve blood outside the body.
...
Wikipedia
