Amlodipine besylate
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /æmˈloʊdəˌpin/ |
| Trade names | Norvasc, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692044 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 64–90% |
| Protein binding | 93% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Metabolites | Various inactive pyrimidine metabolites |
| Onset of action | Highest availability 6–12 hours after oral dose |
| Biological half-life | 30–50 hours |
| Duration of action | At least 24 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.428 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
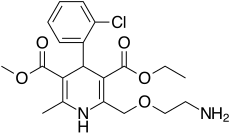
| Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 408.879 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
Amlodipine, sold under the brand name Norvasc among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. While calcium channel blockers are not typically recommended in heart failure, amlodipine may be used if other medications are not sufficient for high blood pressure or heart related chest pain. Amlodipine is taken by mouth and has an effect for at least a day.
Common side effects include: swelling, feeling tired, abdominal pain, and nausea. Serious side effects may include low blood pressure or a heart attack. It is unclear if use is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Doses should be decreased in people with liver problems and in elderly individuals. Amlodipine is a long acting calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine type. It works partly by increasing the size of arteries.
Amlodipine was first patented in 1986 with commercial sale beginning in 1990. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. Wholesale cost in the developing world is 0.003 to 0.066 USD per day for a typical dose as of 2015. In the United States, a month's supply costs less than 25 USD.
Amlodipine is used in the management of hypertension and coronary artery disease in people with either stable angina (where chest pain occurs mostly after physical or emotional stress) or vasospastic angina (where it occurs in cycles) and without heart failure. It can be used as either monotherapy or combination therapy for the management of hypertension or coronary artery disease. Amlodipine can be administered to adults and children 6–17 years of age.
...
Wikipedia
