Amiloride
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Midamor, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Readily absorbed, 15–25% |
| Protein binding | ~23% |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Onset of action | 2 hours (peak at 6–10 hours, duration ~24 hours) |
| Biological half-life | 6 to 9 hours |
| Excretion | urine (20–50%), feces (40%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | MK-870 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.205 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
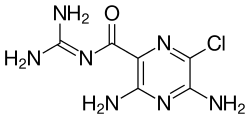
| Formula | C6H8ClN7O |
| Molar mass | 229.627 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Amiloride, sold under the trade name Midamor among others, is a medication typically used with other medications to treat high blood pressure or swelling due to heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver. The medication it is used with often include a thiazide or loop diuretic. It is taken by mouth. Onset of action is about two hours and it lasts for about a day.
Common side effects include high blood potassium, vomiting, loss of appetite, rash, and headache. The risk of high blood potassium is greater in those with kidney problems, diabetes, and those who are older. Amiloride is in the potassium-sparing diuretic family of medications. It works by increase the amount of sodium and decreasing the amount of potassium released by the distal tubule of the kidney.
Amiloride was developed in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. In the United States the wholesale price of a month of medication is about 20.10 USD. In the United Kingdom a month of medication costs the NHS about 24 pounds.
Amiloride is contraindicated in people with Addison's disease, hyperkalaemia, hyponatremia and anuria.
Amiloride's chemical structure contains a guanidinium group containing pyrazine derivative.
...
Wikipedia
