Alphavirus
In biology and immunology, an alphavirus belongs to the group IV Togaviridae family of viruses, according to the system of classification based on viral genome composition introduced by David Baltimore in 1971. Alphaviruses, like all other group IV viruses, have a positive sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are thirty alphaviruses able to infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses as well as invertebrates. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes making the alphaviruses a contributor to the collection of Arboviruses – or Arthropod-Borne Viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical (although slightly pleomorphic), and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.
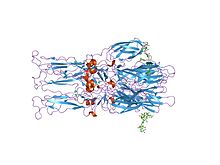
The alphaviruses are small, spherical, enveloped viruses with a genome of a single positive sense strand RNA. The total genome length ranges between 11,000 and 12,000 nucleotides, and has a 5’ cap, and 3’ poly-A tail. The four non-structural protein genes are encoded in the 5′ two-thirds of the genome, while the three structural proteins are translated from a subgenomic mRNA colinear with the 3′ one-third of the genome.
There are two open reading frames (ORF’s) in the genome, non-structural and structural. The first is non structural and encodes proteins (nsP1–nsP4) necessary for transcription and replication of viral RNA. The second encodes three structural proteins: the core nucleocapsid protein C, and the envelope proteins P62 and E1 that associate as a heterodimer. The viral membrane-anchored surface glycoproteins are responsible for receptor recognition and entry into target cells through membrane fusion.
...
Wikipedia