Akkadia
| Akkadian Empire | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
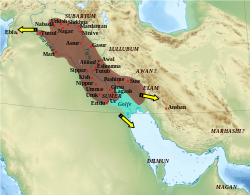
Map of the Akkadian Empire (brown) and the directions in which military campaigns were conducted (yellow arrows)
|
||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Akkad | |||||||||||||||
| Languages | Akkadian | |||||||||||||||
| Religion | Akkadian | |||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||||||||
| šarrum | ||||||||||||||||
| • | c. 2334–2279 BC | Sargon (first) | ||||||||||||||
| • | c. 2170–2154 BC | Shu-turul (last) | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Bronze Age | |||||||||||||||
| • | Established | c. 2334 BC | ||||||||||||||
| • | Conquests of Sargon of Akkad | c. 2340 – 2284 BC | ||||||||||||||
| • | Disestablished | c. 2154 BC | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
Coordinates: 33°6′N 44°6′E / 33.100°N 44.100°E
The Akkadian Empire /əˈkeɪdiən/ was the first ancient Semitic-speaking empire of Mesopotamia, centered in the city of Akkad /ˈækæd/ and its surrounding region, also called Akkad in ancient Mesopotamia in the Bible (Genesis 10:10). The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (modern Bahrain and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.
...
Wikipedia