Adonitol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
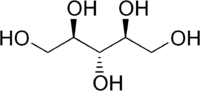
D-ribitol
|
|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3s,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
|
|
| Other names
(2R,3s,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol (not recommended)
Adonit Adonite Adonitol Adonitrol Pentitol 1,2,3,4,5-Pentanepentol 1,2,3,4,5-Pentanol Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.987 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 102 °C (216 °F; 375 K) |
| -91.30·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S22 S24/25 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ribitol or adonitol is a crystalline pentose alcohol (C5H12O5) formed by the reduction of ribose. It occurs naturally in the plant Adonis vernalis, as well as in the cell walls of Gram positive bacteria (specifically, as ribitol phosphate, in teichoic acids). It also contributes to the chemical structure of riboflavin and flavin mononucleotide (FMN), which is a nucleotide coenzyme, present in the enzyme glycolate oxidase.
...
Wikipedia
