Adenomatous
| Adenoma | |
|---|---|
 |
|
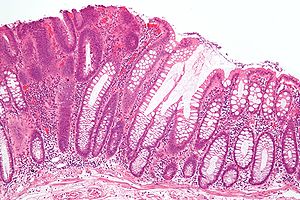
| Micrograph of a tubular adenoma (left of image), a type of colonic polyp and a precursor of colorectal cancer. Normal colorectal mucosa is seen on the right of the image. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| ICD-10 | D12, D35.0, D34, D35.2, and others |
| ICD-9-CM | 211.3, 211.5,223.0, 226, 227.0, |
| ICD-O | M8140/0 |
| MeSH | D000236 |
An adenoma (from Greek αδένας, , "gland" + -ώμα, , "tumor") (/ˌædᵻˈnoʊmə/; plural adenomas or adenomata /ˌædᵻˈnoʊmᵻtə/) is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, over time they may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. But even while benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.
...
Wikipedia
