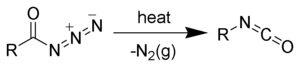Acyl azide
Acyl azides are carboxylic acid derivatives with the general formula RCON3.
Alkyl or aryl acyl chlorides react with sodium azide to give acyl azides.
They can also be synthesized from various carboxylic acids and sodium azide in presence of triphenylphosphine and trichloroacetonitrile catalysts in excellent yields at mild conditions. Another route starts with aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes reacting with iodine azide which is formed from sodium azide and iodine monochloride in acetonitrile.
Acyl azides are used as chemical reagents. On Curtius rearrangement acyl azides yield isocyanates.
Acyl azides are also formed in Darapsky degradation,
...
Wikipedia