Acral lentiginous melanoma
| Acral lentiginous melanoma | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | oncology, dermatology |
| ICD-10 | C43 (ILDS C43.L60) |
| ICD-9-CM | 172.0-173.9 |
| ICD-O | M8744/3 |
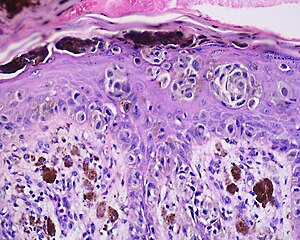
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a kind of lentiginous skin melanoma. Melanoma is a potentially serious skin cancer that arises from pigment cells (melanocytes). Although acral lentiginous melanoma is rare in Caucasians and people with lighter skin types, it is the most common subtype in people with darker skins. Acral lentiginous melanoma is observed on the palms, soles, under the nails and in the oral mucosa. It occurs on non-hair-bearing surfaces of the body, which may or may not be exposed to sunlight. It is also found on mucous membranes. It is the most common form of melanoma diagnosed amongst Asian and sub-Saharan African ethnic groups. The average age at diagnosis is between sixty and seventy years.
Typical signs of acral lentiginous melanoma include the following
Warning signs are new areas of pigmentation, or existing pigmentation that shows change. If caught early, acral lentiginous melanoma has a similar cure rate as the other types of superficial spreading melanoma.
Acral lentiginous melanoma is due as a result of malignant melanocytes. This occurs at the membrane of the skin (outer layers). It should be noted that the pathogenesis of acral lentiginous melanoma remains unknown at this time.
Even though the ideal method of diagnosis of melanoma should be complete excisional biopsy, the location of the melanoma may require alternatives. Dermatoscopy of acral pigmented lesions is very difficult but can be accomplished with diligent attention. Initial confirmation of the suspicion can be done with a small wedge biopsy or small punch biopsy. Thin deep wedge biopsies can heal very well on acral skin, and small punch biopsies can give enough clue to the malignant nature of the lesion. Once this confirmatory biopsy is done, a second complete excisional skin biopsy can be performed with a narrow surgical margin (1 mm). This second biopsy will determine the depth and invasiveness of the melanoma, and will help to define what the final treatment will be. If the melanoma involves the nail fold and the nail bed, complete excision of the nail unit might be required. Final treatment might require wider excision (margins of 0.5 cm or more), digital amputation, lymphangiogram with lymph node dissection, or chemotherapy.
...
Wikipedia
