Acinar
| Acinus | |
|---|---|
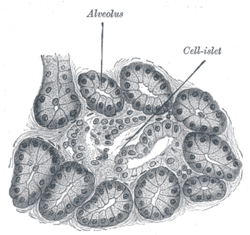
Illustrated section of pancreas of dog. X 250. (Alveolus labeled at center top.)
|
|

Centroacinar cells
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Code | TH H2.00.02.0.03050 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
An acinus (/ˈæsᵻnəs/; plural, acini; adjective, acinar /ˈæsᵻnər/ or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry", such as a raspberry ( is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs.
Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including:
The thyroid follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an endocrine gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion.
Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark.
The term "acinus" is considered synonymous with by some sources, but not all.
The respiratory bronchioles in the lungs terminate in acini, many-lobed sacs containing groupings of alveoli.
...
Wikipedia
