Abruption
| Placental abruption | |
|---|---|
 |
|
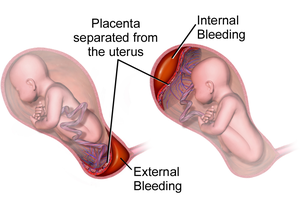
| Illustration depicting internal and external bleeding from placental abruption | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | obstetrics |
| ICD-10 | O45 |
| ICD-9-CM | 641.2 |
| DiseasesDB | 40 |
| MedlinePlus | 000901 |
| eMedicine | med/6 emerg/12 |
| MeSH | D000037 |
Placental abruption, also known as abruptio placentae, is a complication of pregnancy, wherein the placental lining separates from the uterus of the mother prior to delivery. The effects on the mother depend primarily on the severity of the abruption, while the effects on the baby depend on both its severity and the gestational age at which it occurs. The heart rate of the baby is associated with the severity.
Early medical intervention is needed to ensure a good outcome, and this is not available in many parts of the world. Treatment depends on how serious the abruption is and how far along the woman is in her pregnancy.
It is the most common pathological cause of late pregnancy bleeding. In humans, it refers to the abnormal separation after 20 weeks of gestation and prior to birth. It occurs on average in 0.5%, or 1 in 200, deliveries. Placental abruption is a significant contributor to maternal mortality worldwide.
In the early stages of placental abruption, there may be no symptoms. When symptoms develop, they tend to develop suddenly. Common symptoms include sudden-onset abdominal pain, contractions that seem continuous and do not stop, pain in the abdomen and back, vaginal bleeding, enlarged uterus disproportionate to the gestational age of the fetus, decreased fetal movement, and decreased fetal heart rate.
A placental abruption caused by arterial bleeding at the center of the placenta leads to sudden development of severe symptoms and life-threatening conditions including fetal heart rate abnormalities, severe maternal hemorrhage, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Those abruptions caused by venous bleeding at the periphery of the placenta develop more slowly and cause small amounts of bleeding, intrauterine growth restriction, and oligohydramnios (low levels of amniotic fluid).
Risk factors for placental abruption include disease, trauma, history, anatomy, and exposure to substances. The risk of placental abruption increases sixfold after severe maternal trauma. Anatomical risk factors include uncommon uterine anatomy (e.g. bicornuate uterus), uterine synechiae, and leiomyoma. Substances that increase risk of placental abruption include cocaine and tobacco when consumed during pregnancy, especially the third trimester. History of placental abruption or previous Caesarian section increases the risk by a factor of 2.3.
...
Wikipedia
