Abdominal trauma
| Abdominal trauma | |
|---|---|
 |
|
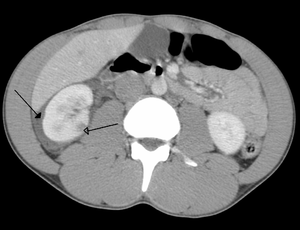
| Abdominal trauma resulting in a right kidney contusion (open arrow) and blood surrounding the kidney (closed arrow) as seen on CT. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | emergency medicine |
| ICD-10 | S30-S39 |
| ICD-9-CM | 868 |
| eMedicine | med/2805 emerg/1 |
| Patient UK | Abdominal trauma |
| MeSH | D000007 |
Abdominal trauma is an injury to the abdomen. It may be blunt or penetrating and may involve damage to the abdominal organs. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness, rigidity, and bruising of the external abdomen. Abdominal trauma presents a risk of severe blood loss and infection. Diagnosis may involve ultrasonography, computed tomography, and peritoneal lavage, and treatment may involve surgery. Injury to the lower chest may cause splenic or liver injuries.
Abdominal trauma is divided into blunt and penetrating types. While penetrating abdominal trauma (PAT) is usually diagnosed based on clinical signs, diagnosis of blunt abdominal trauma is more likely to be delayed or altogether missed because clinical signs are less obvious. Blunt injuries predominate in rural areas, while penetrating ones are more frequent in urban settings. Penetrating trauma is further subdivided into stab wounds and gunshot wounds, which require different methods of treatment.
sign and symptoms are not seen in early days and after some days initial pain is seen. People injured in motor vehicle collisions may present with a "seat belt sign," bruising on the abdomen along the site of the lap portion of the safety belt; this sign is associated with a high rate of injury to the abdominal organs. Seatbelts may also cause abrasions and hematomas; up to 30 percent of people with such signs have associated internal injuries. Early indications of abdominal trauma include nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine, and fever. The injury may present with abdominal pain, tenderness,distension, or rigidity to the touch, and bowel sounds may be diminished or absent. Abdominal guarding is a tensing of the abdominal wall muscles to guard inflamed organs within the abdomen. Pneumoperitoneum, air or gas in the abdominal cavity, may be an indication of rupture of a hollow organ. In penetrating injuries, an evisceration (protrusion of internal organs out of a wound) may be present.
...
Wikipedia
