AP5
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
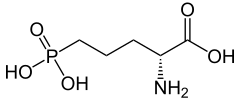
IUPAC name
2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
76326-31-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
119225 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.904 |
| PubChem | 135342 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H12NO5P | |
| Molar mass | 197.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.529 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 482.1 °C (899.8 °F; 755.2 K) |
| Ammonium hydroxide, 50 mg/mL | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
AP5 or APV ((2R)-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid; (2R)-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate) is a selective NMDA receptor antagonist that competitively inhibits the ligand (glutamate) binding site of NMDA receptors. AP5 blocks NMDA receptors in micromolar concentrations (~50 µM).
AP5 blocks the cellular analog of classical conditioning in the sea slug Aplysia californica, and has similar effects on Aplysia long-term potentiation (LTP), since NMDA receptors are required for both. It is sometimes used in conjunction with the calcium chelator BAPTA to determine whether NMDARs are required for a particular cellular process. AP5/APV has also been used to study NMDAR-dependent LTP in the mammalian hippocampus.
In general, AP5 is very fast-acting within in vitro preparations, and can block NMDA receptor action at a reasonably small concentration. The active isomer of AP5 is considered to be the D configuration, although many preparations are available as a racemic mixture of D- and L-isomers. It is useful to isolate the action of other glutamate receptors in the brain, i.e., AMPA and kainate receptors.
AP5 can block the conversion of a silent synapse to an active one, since this conversion is NMDA receptor-dependent.
AP5 was developed by Jeff Watkins and Harry Olverman.
Works cited
^ Laube, B; Hirai H, Sturgess M, Betz H, and Kuhse J (1997). "Molecular determinants of antagonists discrimination by NMDA receptor subunits: Analysis of the glutamate binding site on the NR2B subunit". Neuron 18 (3): 493–503. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81249-0. PMID 9115742.
...
Wikipedia
