A-flat minor
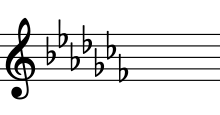 |
|
| Relative key |
C♭ major enharmonic: B major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | A♭ major |
| Dominant key |
E♭ minor enharmonic: D♯ minor |
| Subdominant |
D♭ minor enharmonic: C♯ minor |
| Enharmonic | G♯ minor |
| Component pitches | |
| A♭, B♭, C♭, D♭, E♭, F♭, G♭, A♭ | |
A-flat minor is a minor scale based on A-flat, consisting of the pitches A♭, B♭, C♭, D♭, E♭, F♭, and G♭. For the harmonic minor, the G♭ is raised to G♮. Its key signature has seven flats (see below: Scales and keys).
Its relative major is C♭ major (or, enharmonically, B major), and its parallel major is A♭ major. Its direct enharmonic equivalent is G♯ minor.
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary.
Although A-flat minor occurs in modulation in works in other keys, it is only rarely used as the principal key of a piece of music. Some well-known uses of the key in classical and romantic piano music include:
It is also used in Frederick Loewe's score to the 1956 musical play My Fair Lady; the Second Servants' Chorus is set in A-flat minor (the preceding and following choruses being a semitone lower and higher respectively).
...
Wikipedia
