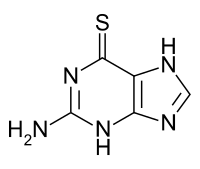
6-thioguanine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lanvis, Tabloid, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a682099 |
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% (range 14% to 46%) |
| Metabolism | Intracellular |
| Biological half-life | 80 minutes (range 25-240 minutes) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.299 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H5N5S |
| Molar mass | 167.193 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tioguanine, also known as thioguanine or 6-thioguanine (6-TG) is a medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Long term use is not recommended. It is given by mouth.
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, liver problems and inflammation of the mouth. It is recommended that liver enzymes be checked weekly when on the medication. People with a genetic deficiency in thiopurine S-methyltransferase are at higher risk of side effects. Avoiding pregnancy when on the medication is recommended for both males and females. Tioguanine is in the antimetabolite family of medications. It is a purine analogue of guanine and works by disrupting DNA and RNA.
Tioguanine was between 1949 and 1951. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale price in the developing world is about 7.07 USD per 40 mg pill as of 2014. In the United Kingdom this amount costs the NHS about 4.14 pounds.
The major concern that has inhibited the use of thioguanine has been veno-occlusive disease (VOD) and its histological precursor nodular regenerative hyperplasia (NRH). The incidence of NRH with thioguanine was reported as between 33-76%. The risk of ensuing VOD is serious and frequently irreversible so this side effect has been a major concern. However, recent evidence using an animal model for thioguanine-induced NRH/VOD has shown that, contrary to previous assumptions, NRH/VOD is dose dependent and the mechanism for this has been demonstrated. This has been confirmed in human trials, where thioguanine has proven to be safe but efficacious for coeliac disease when used at doses below those commonly prescribed. This has led to a revival of interest in thioguanine because of its higher efficacy and faster action compared to other thiopurines and immunosuppressants such as mycophenylate.
...
Wikipedia
