5S rRNA
| 5S ribosomal RNA | |
|---|---|
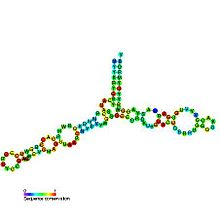
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of 5S ribosomal RNA
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | 5S_rRNA |
| Rfam | RF00001 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; rRNA |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota; Bacteria; Archaea |
| GO | 0005840 0003735 |
| SO | 0000652 |
The 5S ribosomal RNA (5S rRNA) is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life (bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes), with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule’s sedimentation velocity in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S).
In prokaryotes, the 5S rRNA gene is typically located in rRNA operons downstream of the small and large subunit rRNA, and co-transcribed into a polycistronic precursor. A particularity of eukaryotic nuclear genomes is the occurrence of multiple 5S rRNA gene copies (5S rDNA) clustered in tandem repeats, with copy number varying from species to species. Eukaryotic 5S rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase III, whereas other eukaroytic rRNAs are cleaved from a 45S precursor transcribed by RNA polymerase I. In Xenopus oocytes, it has been shown that fingers 4-7 of the nine-zinc finger transcription factor TFIIIA can bind to the central region of 5S RNA. Binding between 5S rRNA and TFIIIA serves to both repress further transcription of the 5S RNA gene and stabilize the 5S RNA transcript until it is required for ribosome assembly.
...
Wikipedia
