4th ventricle
| Fourth ventricle | |
|---|---|

Scheme showing relations of the ventricles to the surface of the brain. (Fourth ventricle labeled at bottom center.)
|
|
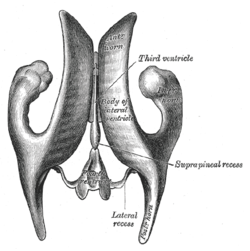
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from above. (Fourth ventricle visible at bottom center.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ventriculus quartus |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.276.500 |
| NeuroNames | hier-617 |
| NeuroLex ID | Fourth ventricle |
| TA | A14.1.05.701 |
| FMA | 78469 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius) to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the pons or in the upper part of the medulla. CSF entering the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct can exit to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord through two lateral apertures and a single, midline median aperture.
The fourth ventricle has a "roof" dorsally a "floor" ventrally, and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles. The roof of the fourth ventricle is formed by the cerebellum (superior and inferior medullary vela). The fastigium, (Latin for summit), is used to refer to the peak of the fourth ventricle.The fastigial nucleus lies immediately above the roof of the fourth ventricle.
The floor of the fourth ventricle is formed by the rhomboid fossa. Among the prominent features of the floor of the fourth ventricle are the:
...
Wikipedia
