4-8-0
Front of locomotive at left
|
|||||||||||||||
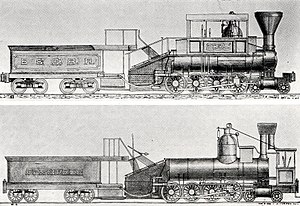
The Centipede as built (bottom) and as modified by the B&O Railroad (top)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Equivalent classifications | |
|---|---|
| UIC class | 2′D |
| French class | 240 |
| Turkish class | 46 |
| Swiss class | 4/6 |
| Russian class | 2-4-0 |
| First known tank engine version | |
|---|---|
| First use | 1909 |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Locomotive | NER Class X |
| Railway | North Eastern Railway |
| Designer | Wilson Worsdell |
| Builder | North Eastern Railway |
| First known tender engine version | |
|---|---|
| First use | 1855 |
| Country | United States of America |
| Locomotive | B&O no. 235 Centipede |
| Railway | Baltimore and Ohio Railroad |
| Designer | Ross Winans |
| Builder | Ross Winans |
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, usually in a leading truck or bogie, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. In North America and in some other countries the type was usually known as the Mastodon and sometimes as the Twelve-wheeler.
The very first 4-8-0 locomotive is believed to have been the Centipede, a tender locomotive built by Ross Winans in 1855 for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in the United States of America, where it remained in service for nearly twenty years. It appears to have been delivered in a cab-forward type of configuration that was modified to a Camel configuration in 1864. On a Camel locomotive the cab was mounted atop the boiler, unlike the later Camelback locomotive whose cab straddled the boiler and that first appeared around 1877.
The name Mastodon for the 4-8-0 wheel arrangement was derived from the unofficial name of the first 4-8-0 locomotive of the Central Pacific Railroad in the United States, the wood-fired CPR no. 229, which was designed and built in 1882 by the railroad's master mechanic, Andrew Jackson (A.J.) Stevens, at the railroad’s Sacramento works in California.
The 4-8-0 wheel arrangement saw service in Australia from 1900. In Tasmania, the privately owned Emu Bay Railway ordered four 4-8-0 tender locomotives for their 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge system. In 1911, another locomotive was delivered from the North British Locomotive Company. Two of these locomotives are preserved.
...
Wikipedia
