17α-hydroxyprogesterone caproate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Proluton, Proluton Depot, Makena, others |
| Synonyms | OHPC; Hydroxyprogesterone hexanoate; 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone caproate; 17α-OHPC; 17-Hydroxyprogesterone caproate; 17-OHPC; 17-HPC; 17α-HPC; HPC |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intramuscular injection |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability |
Oral: Very low (~3% in rats) Intramuscular: 100% (in rats) |
| Biological half-life | Non-pregnant: 7.8 days Singlet: 16 days Twins: 10 days |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.127 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
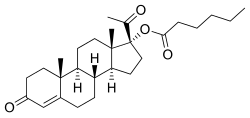
| Formula | C27H40O4 |
| Molar mass | 428.6041 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate (OHPC), sold under the brand names Proluton, Proluton Depot, and Makena among others, is a progestin which is used in the treatment of a variety of gynecological disorders and for specific obstetric indications. It was previously marketed under the trade name Delalutin by Squibb, which was approved by the United States (U.S.) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1956 and withdrawn from marketing in 1999. It is also sold as Proluton throughout Europe. The U.S. FDA approved Makena from KV Pharmaceutical on February 4, 2011 for prevention of preterm delivery in women with a history of preterm delivery, sparking a pricing controversy. OHPC is not active by mouth and must be administered by injection into muscle.
OHPC is used in the treatment of threatened miscarriage, gynecological disorders such as dysmenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome, fibrocystic breast disease, adenosis, and breast pain, and endometrial cancer. It was used widely in the 1950s through the 1970s for these indications, but OHPC more recently has received the most attention in the prevention of preterm birth.
...
Wikipedia
