12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
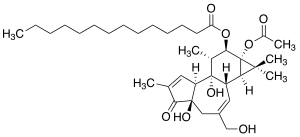
(1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-9a-(acetyloxy)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9,9a-decahydro-H-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9-yl myristate
|
|
| Other names
TPA, PMA, Phorbol myristate acetate,
Tetradecanoylphorbol acetate. |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.109.485 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C36H56O8 | |
| Molar mass | 616.83 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also commonly known as tetradecanoylphorbol acetate, tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), is a diester of phorbol and a potent tumor promoter often employed in biomedical research to activate the signal transduction enzyme protein kinase C (PKC). The effects of TPA on PKC result from its similarity to one of the natural activators of classic PKC isoforms, diacylglycerol. TPA is a small molecule drug.
In ROS biology, superoxide was identified as the major reactive oxygen species induced by TPA/PMA but not by ionomycin in mouse macrophages. Thus, TPA/PMA has been routinely used as an inducer for endogenous superoxide production.
TPA is also being studied as a drug in the treatment of hematologic cancer
TPA has a specific use in cancer diagnostics as a B-cell specific mitogen in cytogenetic testing. To view the chromosomes, a cytogenetic test requires dividing cells. TPA is used to stimulate division of B-cells during cytogenetic diagnosis of B-cell cancers such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
TPA is also commonly used together with ionomycin to stimulate T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production, and is used in protocols for intracellular staining of these cytokines.
TPA induces KSHV reactivation in PEL cell cultures via stimulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. The pathway involves the activation of the early-immediate viral protein RTA that contributes to the activation of the lytic cycle.
...
Wikipedia
