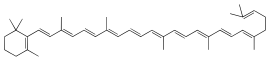
Γ-carotene
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
β,ψ-Carotene
|
|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
2-((1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E,19E)-3,7,12,16,20,24-hexamethylpentacosa-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,23-undecaen-1-yl)-1,3,3-trimethylcyclohex-1-ene
|
|
| Other names
β,psi-Carotene
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C40H56 | |
| Molar mass | 536.89 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 160 to 162 °C (320 to 324 °F; 433 to 435 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
γ-Carotene is a carotenoid, and is a biosynthetic intermediate for cyclized carotenoid synthesis in plants. It is formed from cyclization of lycopene by lycopene cyclase epsilon. Along with several other carotenoids, γ-Carotene is a vitamer of vitamin A in herbivores and omnivores. Carotenoids with a cyclized, beta-ionone ring can be converted to vitamin A, also known as retinol, by the enzyme Beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase; however, the bioconversion of gamma-carotene to retinol has not been well-characterized.
...
Wikipedia
