Grasshopper 3D
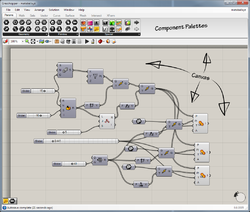
A sample program in the Grasshopper GUI
|
|
| Developer(s) | Robert McNeel & Associates |
|---|---|
| Initial release | September 2007 |
| Stable release |
1.0 / April 4, 2014
|
| Operating system | Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7/8/10) |
| Type | Visual Programming |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | www |
Grasshopper is a visual programming language and environment developed by David Rutten at Robert McNeel & Associates, that runs within the Rhinoceros 3D computer-aided design (CAD) application. Programs are created by dragging components onto a canvas. The outputs to these components are then connected to the inputs of subsequent components.
Grasshopper is primarily used to build generative algorithms, such as for generative art. Many of Grasshopper's components create 3D geometry. Programs may also contain other types of algorithms including numeric, textual, audio-visual and haptic applications.
Advanced uses of Grasshopper include parametric modelling for structural engineering, parametric modelling for architecture and fabrication, computational Japanese garden design, lighting performance analysis for eco-friendly architecture and building energy consumption.
The first version of Grasshopper was released in September 2007, and titled Explicit History. Grasshopper has become part of the standard Rhino toolset in Rhino 6.0 and later.
AEC Magazine stated that Grasshopper is "Popular among students and professionals, McNeel Associate’s Rhino modelling tool is endemic in the architectural design world. The new Grasshopper environment provides an intuitive way to explore designs without having to learn to script."
Grasshopper features an advanced user interface. The main window consist mainly of the component 'palettes' and the 'canvas'. Since Grasshopper is a plug-in to Rhinoceros 3D, the layout of the main window is kept minimal.
GUI elements include:
The main interface for algorithm design in Grasshopper is the node-based editor. Data is passed from component to component via connecting wires which always connect an output grip with an input grip. Data can either be defined locally as a constant, or it can be imported from the Rhino document or a file on the computer. Data is always stored in parameters, which can either be free-floating or attached to a component as input and outputs objects.
...
Wikipedia

