Anterior commissure
| Anterior commissure | |
|---|---|

Coronal section of brain through anterior commissure. (Label for "anterior commissure" is on left, third from bottom.)
|
|
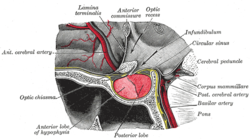
The hypophysis cerebri in position. Shown in sagittal section. (Caption for anterior commissure is at center top.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | commissura anterior |
| NeuroNames | hier-187 |
| NeuroLex ID | Anterior Commissure |
| TA | A14.1.08.421 |
| FMA | 61961 62053, 61961 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a bundle of nerve fibers (white matter), connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. The great majority of fibers connecting the two hemispheres travel through the corpus callosum, which is over 10 times larger than the anterior commissure, and other routes of communication pass through the hippocampal commissure or, indirectly, via subcortical connections. Nevertheless, the anterior commissure is a significant pathway that can be clearly distinguished in the brains of all mammals. The anterior commissure plays a key role in pain sensation, more specifically sharp, acute pain. It also contains decussating fibers from the olfactory tracts, vital for the sense of smell and chemoreception. The anterior commissure works with the posterior commissure to link the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain and also interconnects the amygdalas and temporal lobes, contributing to the role of memory, emotion, speech and hearing. It also is involved in olfaction, instinct, and sexual behavior.
In a sagittal section, the anterior commissure is oval in shape, having a long vertical axis that measures about 5 mm.
The fibers of the anterior commissure can be traced laterally and posteriorly on either side beneath the corpus striatum into the substance of the temporal lobe.
It serves in this way to connect the two temporal lobes, but it also contains decussating fibers from the olfactory tracts, and is a part of the neospinothalamic tract for pain. The anterior commissure also serves to connect the two amygdala.
The corpus callosum allows for communication between the two hemispheres and is found only in placental mammals (the eutherians), while it is absent in monotremes and marsupials, as well as other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. The anterior commissure serves as the primary mode of interhemispheric communication in marsupials, and which carries all the commissural fibers arising from the neocortex (also known as the neopallium), whereas in placental mammals the anterior commissure carries only some of these fibers).
...
Wikipedia
